Systemic urate deposition exclusive of the extremities: summary of published evidence
P. Khanna, B. LaMoreaux, A. Kumar
Affiliation(s):
University of Michigan; Horizon Therapeutics; Horizon Therapeutics
Background: Gout is the most common adult inflammatory arthropathy. Although tophi are the defining clinical feature of this debilitating disease, systemic urate deposition in major organ systems remains unrecognized. While numerous co-morbidities including renal disease, cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome are often associated with gout, a casual role has yet to be established. We hypothesize that urate deposition in these organs triggers an inflammatory response resulting in chronic subclinical inflammation and subsequent tissue damage. However, direct urate deposition in various organ systems needs to be first demonstrated to provide the potential link for causality in these systemic disorders.
Objectives: To review the published literature for evidence of urate deposition exclusive of the extremities in patients with gout based on autopsy, clinical exam, surgery, histopathology and imaging reports.
Methods: PUBMED from 1920 to 2019 was searched to identify articles documenting non-extremity urate deposition.
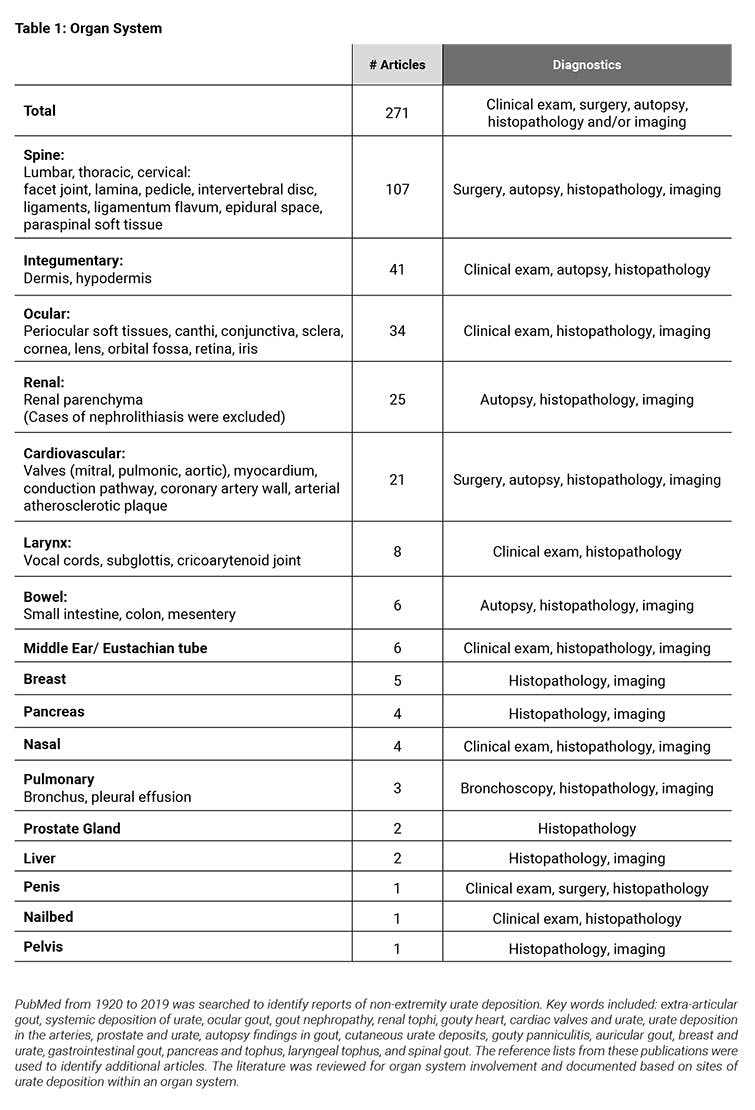
Results: There were 271 case reports documenting extra-articular urate deposition confirmed by autopsy, histopathology, surgery, clinical exam and/or radiology imaging. Urate deposition was reported in multiple organ systems (Table 1) including the spine, integumentary, ocular, renal, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, larynx, breast, middle ear, pancreas, nasal, prostate gland, liver, pulmonary, penis, nailbed, and pelvis.
Conclusion: There is a growing body of literature reporting systemic urate deposition documented by clinical exam, surgery, autopsy, histopathology, and imaging findings. Urate crystal deposition with the formation of tophi and micro-tophi involve multiple organ systems including cardiovascular, renal, spine, integumentary, prostate, bowel, pancreas, eyes, pelvic, breast, lungs, middle ear, larynx, liver, penis, nailbed, and nose. Given the strong association of gout with various comorbidities, there is a critical need for dedicated investigation to determine the resulting clinical sequelae of systemic urate deposition with respect to ongoing subclinical inflammation and potential end-organ damage.
Keywords: extra-articular gout, systemic deposition of urate, ocular gout, gout nephropathy, renal tophi, gouty heart, cardiac valves and urate, urate deposition in the arteries, prostate and urate, autopsy findings in gout, cutaneous urate deposits, gouty panniculitis, auricular gout, breast and urate, gastrointestinal gout, pancreas and tophus, laryngeal tophus, and spinal gout. The reference lists from these publications were also used to identify additional articles. The literature was reviewed for organ system involvement and documented based on sites of urate deposition within an organ system.
References: 1. Klauser, A, et al. JAMA Cardiology. 2019 Sept 11. 2. Nickeleit, V et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997; 12:1832-1838. 3. Ao, J, et al. Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology. 2017; 45: 73–80 4. Toprover, M. et al. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015; 17:70.